The Rise of AI-Augmented Product Teams: Skills Every PM Must Learn by 2026
Three months ago, I watched a Series B startup compress what normally takes eight weeks into three.
Same product team. Same roadmap complexity. But something had shifted.
The PM wasn't drowning in documentation. The engineers weren't context-switching between twelve half-finished features. Sprint planning took 45 minutes instead of three hours.
The difference? They'd learned to work with AI as a teammate, not just a tool.

The evolution of product management: From traditional skills to AI-augmented capabilities by 2026
Why This Matters Now
Here's the uncomfortable truth: AI isn't replacing product managers. But it's fundamentally redefining what "good" looks like.
Gen AI adoption has doubled to 65% in just one year. Product teams using these tools save 18 hours per sprint and cut meetings by 26 per month. Yet nearly half of PMs learned AI skills on their own—using AI tools 11 times daily without formal training.
That's like learning to fly while the plane is already in the air.
By 2026, the gap between AI-fluent PMs and those still relying on traditional methods will be impossible to close.
The question isn't whether you need AI skills. It's which ones will separate leaders from those left behind.
The Current Landscape: AI in Product Management Today

Key AI tools transforming product management: BuildBetter, Jira AI, ChatPRD, and Notion AI
The AI transformation of product management is already well underway. In 2024, global AI spending reached $500 billion, up 19% from the previous year, with the AI in software development market projected to grow from $674.3 million to $15.7 billion by 2033 at a staggering 42.3% compound annual growth rate.
What does this mean for product teams? Each dollar invested in Gen AI is delivering $3.70 back, with revenue increases most commonly reported in marketing and sales, strategy and corporate finance, and product and service development. Companies integrating AI are experiencing approximately 20% higher sales and a 22% increase in market valuation.
The tools transforming product management include:
- BuildBetter.ai: Converts unstructured data into insights, enabling data-driven decision-making at unprecedented speed
- Jira AI: Powered by Atlassian Intelligence, it automates project tracking and delivers smart insights. A global financial services firm reported 20% faster project completion rates and 15% lower budget overruns
- ChatPRD: Acts as an on-demand Chief Product Officer, drafting detailed product requirements documents that meet high-quality standards
- Notion AI and Productboard AI: Assist with documentation, sprint planning, and feature prioritization
These tools are not just making existing workflows faster. They are enabling entirely new capabilities, such as predicting product success metrics before launch by analyzing historical data, market conditions, and user behavior to forecast adoption rates, retention, and revenue potential.
Essential Technical Skills
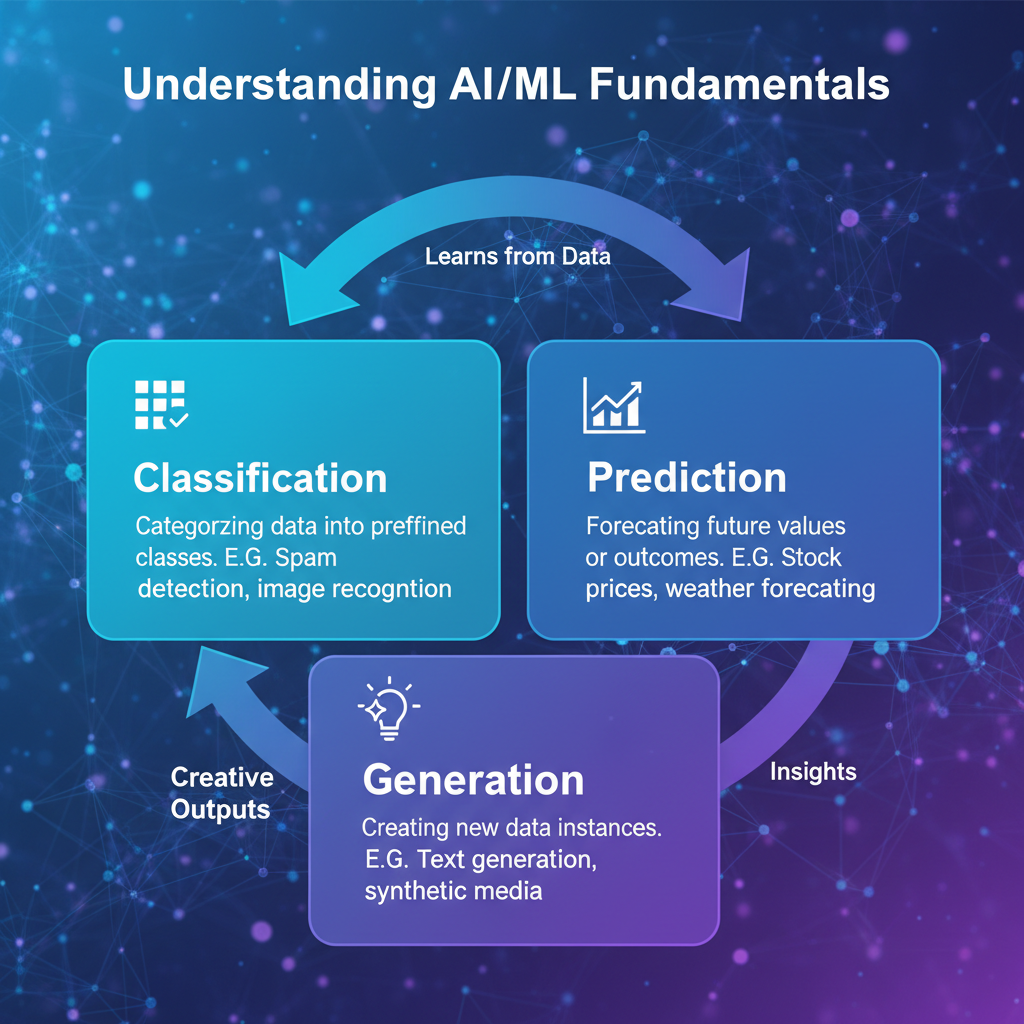
Core AI/ML concepts every product manager needs to understand: Classification, Prediction, and Generation
Understanding AI/ML Fundamentals (Without Becoming a Data Scientist)
The most critical technical skill for product managers is developing a solid grasp of AI and machine learning concepts without needing to become data scientists themselves. This means understanding:
- Different AI model types: Knowing when to use classification, ranking, prediction, or generation tasks
- Machine learning algorithms: Understanding the basics of supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning
- Probabilistic systems: Recognizing that AI systems are inherently probabilistic, not deterministic
The key is identifying opportunities where machine learning or generative AI is the right fit and translating business and user problems into appropriate AI tasks. You need to ask informed questions like: "What training data do we need?" "How will we measure model performance?" "What are the edge cases where our model might fail?"
Prompt Engineering and Working with LLMs
Prompt engineering has emerged as one of the most practical and immediately valuable skills for product managers. When you feed generative AI a well-structured prompt, it can deliver highly relevant, well-written outputs faster than you could draft yourself, whether summarizing a user research session or writing documentation.
The core principles of effective prompt engineering include:
- Provide clear and specific instructions: Be explicit about format, tone, and constraints
- Give the model time to process: For complex tasks, break them into sequential steps
- Use examples: Show the model what good output looks like
- Iterate and refine: Treat prompts as products themselves that need testing and optimization
Product managers should become familiar with prompt management platforms like Agenta, Langfuse, and tools such as IBM Watsonx that enable sophisticated prompt engineering approaches.
Data Literacy and Analytics
Knowing the right questions to ask about customer data is an entirely new PM skillset. Having hands-on experience or working knowledge of data and models as an AI PM is considered essential by AI experts. This includes:
- Understanding data quality and its impact on model performance
- Interpreting model metrics like precision, recall, and F1 scores
- Recognizing bias in training data and its downstream effects
- Making decisions based on probabilistic outputs rather than deterministic rules
The most successful AI product managers can bridge the gap between raw data, model outputs, and business value, translating technical metrics into product decisions.
Strategic AI Skills
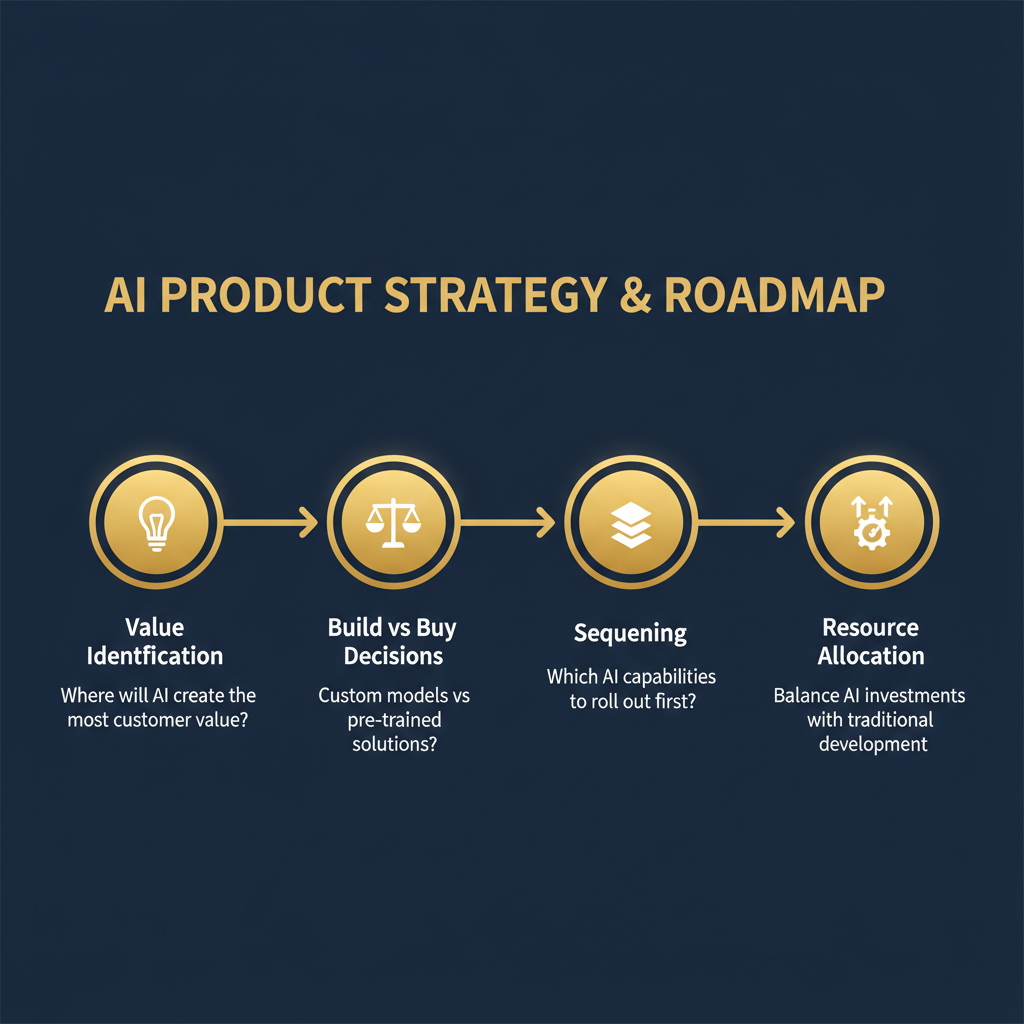
Strategic AI product roadmap: From value identification to resource allocation
AI Product Strategy and Roadmapping
Developing a strategic product vision is critical for AI product managers. This involves identifying opportunities for AI integration that align with business goals and solve real-world problems, staying abreast of AI trends, and recognizing the potential impact of emerging technologies.
Key strategic considerations include:
- Value identification: Where will AI create the most customer or business value?
- Build vs. buy decisions: When should you build custom models versus using pre-trained solutions?
- Sequencing: What AI capabilities should you roll out first to build momentum?
- Resource allocation: How do you balance AI investments with traditional product development?
The data shows that only 22% of companies have implemented an AI strategy and built advanced capabilities that generate substantial gains. Strategic clarity separates these leaders from the 74% of companies that have yet to show tangible value from AI.
Ethical AI Considerations and Bias Mitigation
As AI systems become more powerful and pervasive, product managers must become stewards of ethical AI development. This includes:
- Identifying and mitigating bias: Understanding how bias enters training data and model design
- Ensuring fairness: Designing systems that work equitably across different user groups
- Transparency: Communicating when and how AI is being used in products
- Privacy: Protecting user data while leveraging it for model training
Setting clear expectations around model failure modes, confidence levels, and fallback strategies is essential. Users need to understand when they're interacting with AI and what limitations exist.
AI Governance and Compliance
The complexity, scale, and accountability of PM work with AI exceed what informal learning can reliably provide. Product managers need to understand:
- Regulatory requirements around AI in their industry
- Documentation and audit trail requirements for AI systems
- Risk management frameworks for AI deployment
- Security considerations specific to AI systems
Nearly one-third of employees report being distinctly uncomfortable with AI in their roles, making governance and clear policies essential for adoption.
Collaborative Skills
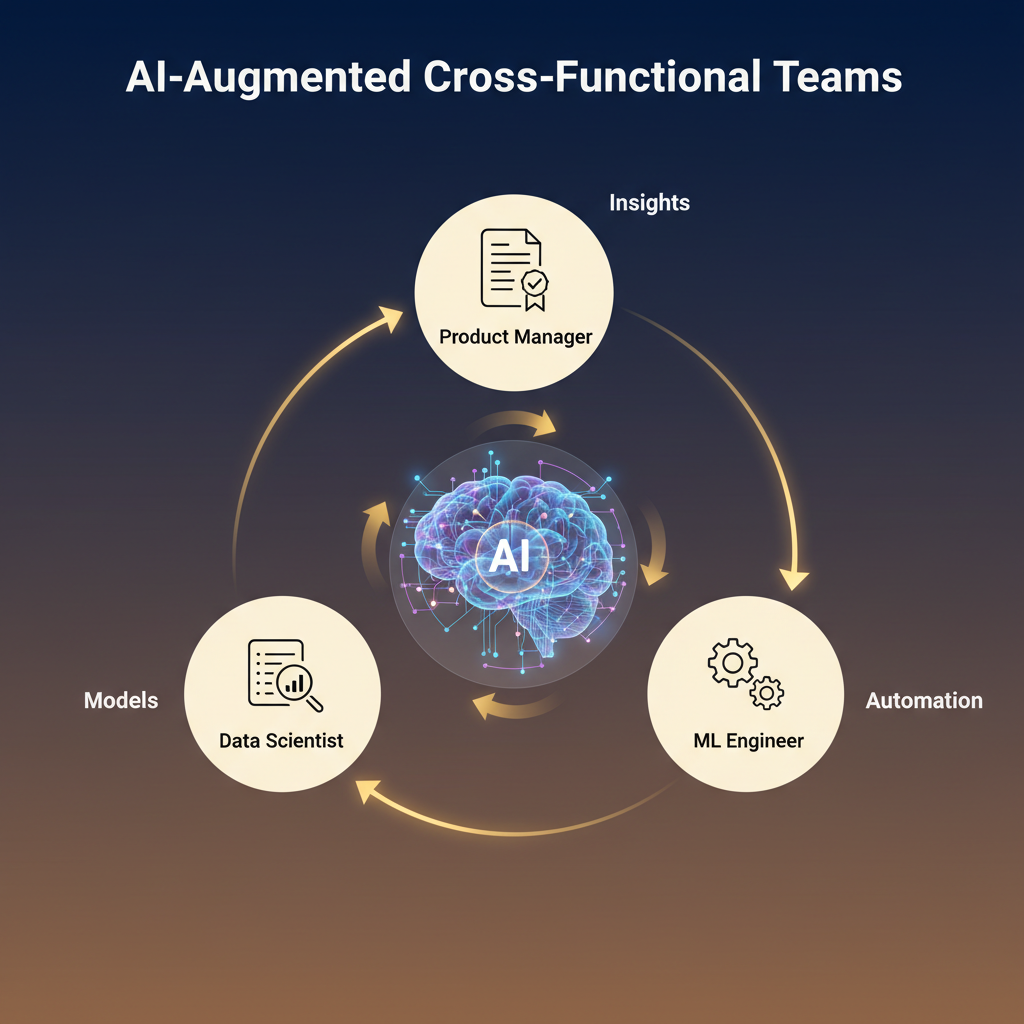
Cross-functional collaboration: Product Managers, Data Scientists, and ML Engineers working together
Working with AI-Augmented Teams
The nature of product teamwork is fundamentally changing. Projects that previously required months of coordination between functions can now be completed by smaller, AI-augmented teams in weeks. This requires new collaboration patterns:
- Redefining roles: Understanding what tasks AI can handle versus where human judgment is irreplaceable
- Managing "cybernetic teammates": Working with AI as a team member, not just a tool
- Asynchronous collaboration: Leveraging AI to reduce meeting overhead while maintaining alignment
The evidence shows AI is augmenting rather than replacing team members, with 26% of teams actually expanding while achieving higher productivity.
Cross-Functional Collaboration with Data Scientists and ML Engineers
Product managers must collaborate effectively with data scientists, engineers, and other stakeholders to ensure AI solutions are integrated smoothly and add value to the user experience. This means:
- Speaking the language of data science without claiming expertise
- Understanding the constraints and possibilities of different ML approaches
- Facilitating communication between technical and non-technical stakeholders
- Managing expectations around model development timelines and capabilities
Managing Human-AI Workflows
Designing products that seamlessly blend human and AI capabilities is an emerging skill. This includes:
- Identifying which decisions should be fully automated versus requiring human oversight
- Designing interfaces for AI-assisted work
- Creating feedback loops that improve AI performance over time
- Managing the change management process as workflows evolve
Practical AI Tools PMs Should Master
By 2026, product managers should have hands-on experience with several categories of AI tools:
AI-Powered Analytics Tools
- Natural language query interfaces for data exploration
- Automated insight generation from user behavior data
- Predictive analytics for feature success and churn risk
Automation and Workflow Tools
- AI-powered project management and sprint planning
- Automated documentation generation
- Intelligent task routing and prioritization
AI Assistants for Product Management
- Tools like ChatPRD for requirements documentation
- AI-powered user research synthesis
- Competitive intelligence gathering and analysis
Emerging Capabilities
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for knowledge management
- Multi-step agents for complex workflows
- Real-time sentiment analysis across customer feedback channels
Getting Started: A Learning Roadmap
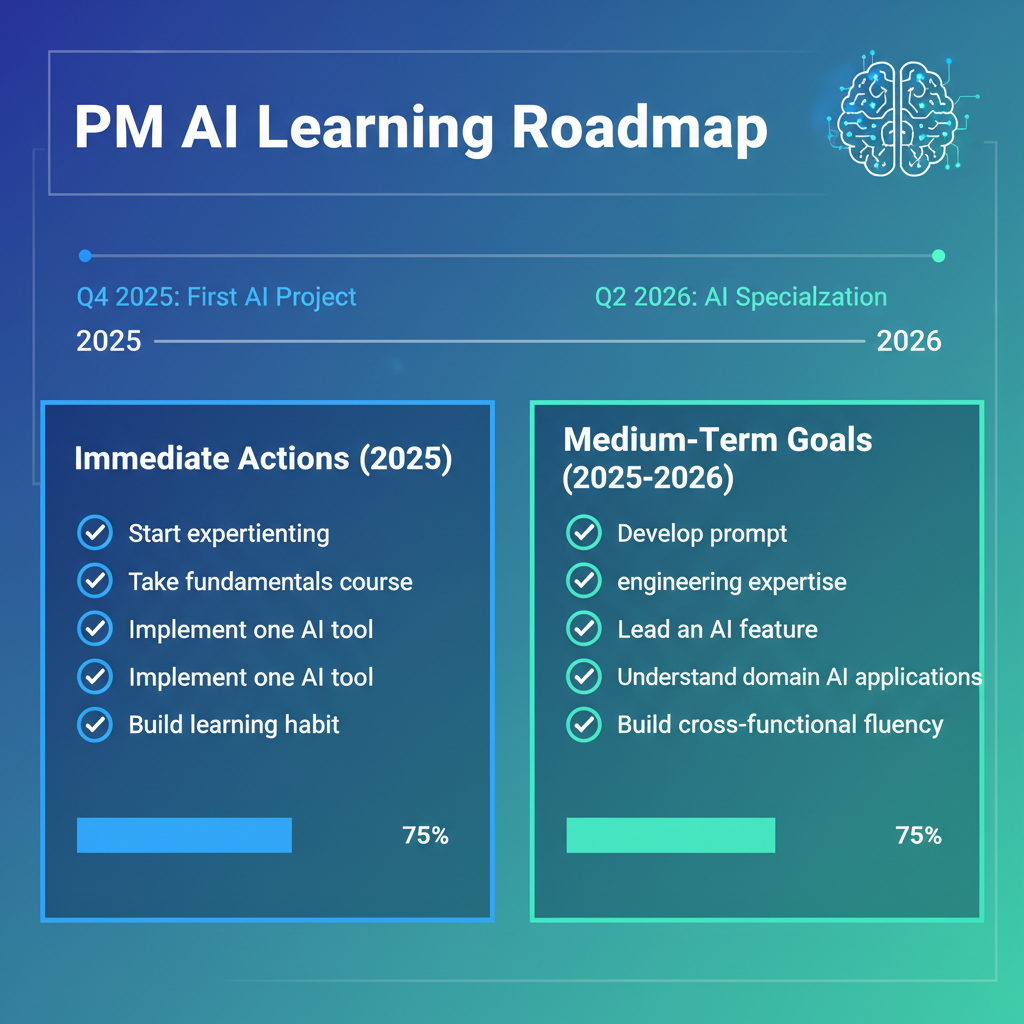
Your AI learning journey: From immediate actions to medium-term mastery by 2026
Immediate Actions (2025)
- Start experimenting: Use ChatGPT, Claude, or other LLMs daily for actual work tasks
- Take a fundamentals course: Complete an introductory AI/ML course (Coursera offers specialized programs for product managers)
- Implement one AI tool: Choose a tool like Notion AI or Jira AI and become proficient
- Build a learning habit: Dedicate 30 minutes daily to AI skill development
Medium-Term Goals (2025-2026)
- Develop prompt engineering expertise: Practice advanced prompting techniques and learn prompt management
- Lead an AI feature: Take ownership of at least one AI-powered product feature from concept to launch
- Understand your domain's AI applications: Deep dive into how AI is transforming your specific industry
- Build cross-functional AI fluency: Shadow data scientists and ML engineers to understand their workflows
Resources and Certifications
- AI Product Management 101 by Dr. Marily Nika on Maven
- Generative AI for Product Managers specialization on Coursera
- AI & ML courses from Simplilearn, ProductSchool, and ELVTR
- Community engagement: Join AI product management communities and attend conferences
The average time to deploy AI is less than 8 months, meaning you can see results from your learning investments quickly.
The Path Forward
Here's what I've learned after two decades in product: tools evolve, but principles don't.
The best PMs have always been translators—between business and tech, between vision and execution, between what's possible and what's practical.
AI doesn't change that. It amplifies it.
The product managers who thrive in 2026 won't be those who know the most about AI. They'll be those who use AI to make better decisions faster, ship with more confidence, and free up mental space for the strategic thinking that actually matters.
Each dollar invested in Gen AI delivers $3.70 in returns. Teams are shipping faster, with better insights, and with half the overhead.
But none of that happens by accident.
Start today. Pick one AI tool and use it for a week. Take that first course. Lead that first AI feature. Document what you learn and share it with your team.
By 2026, these capabilities won't be differentiators—they'll be baseline expectations.
The future of product management is augmented, intelligent, and accelerated. The question is whether you'll be leading it or catching up to it.
Your next move: Block one hour this week to experiment with ChatGPT or Claude for actual product work—drafting PRDs, synthesizing user research, or planning sprints. Don't just read about AI. Use it.